SGPlan 4: Subgoal Partitioning and Resolution in Planning
Yixin Chen , Chih-Wei Hsu , and Benjamin W. Wah
For bug reports and problems on using the programs, please send email to Chih-wei Hsu
Winner of the International Planning Competition (IPC) 2004 classic part:
· 1st Prize, Suboptimal Temporal Metric Track
·
2nd Prize,
Suboptimal Propositional Track
Summary of Competition Results (June, 2004)
|
|
SGPlan 4 |
LPG-TD |
Downward |
Diagonally |
Macro-FF |
YAHSP |
Crikey |
|
Propositional Domains (1st / 2nd Places) |
4 / 6 |
1 / 6 |
6 / 1 |
7 / 2 |
3 / 0 |
4 / 2 |
0 / 1 |
|
Temporal/Metric Domains (1st / 2nd Places) |
13 / 0 |
9 / 4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total Count (1st / 2nd Places) |
17 / 6 |
10 / 10 |
6 / 1 |
7 / 2 |
3 / 0 |
4 / 2 |
0 / 1 |
Details of competition results
The binary files of SGPlan 4 are available for download. (The June 2004 Linux version was compiled using gcc version 3.2.3 on Redhat Enterprise Linux 3 and with the static linking option; the others were compiled using gcc version 3.4.5 on Redhat Enterprise Linux 4.)
Instructions for running SGPlan 4:
- Download
- Version 4.0
(June 2004 version used in IPC4, with PERT scheduling in benchmarks with TIL and deadlines),
- Version 4.1 (August 2006 version used in our JAIR2006 paper, with PERT scheduling in all benchmarks).
- Version 4.2 (August 2006 version used in our JAIR2006 paper, with PERT scheduling in all benchmarks and a new version of FF).
- Version 4.0
(June 2004 version used in IPC4, with PERT scheduling in benchmarks with TIL and deadlines),
- Uncompress the downloaded file
in the current directory by running
unzip
This will create three files in the current directory: sgplan, p01-domain.pddl, and p01-s2-n1-l2-f50.pddl. - Run sgplan:
Usage: sgplan -o operator_file_name -f fact_file_name [-out solution_file_name] [-cputime seconds]
where the output will go to the standard output if the "-out solution_file_name" option is not specified,
and the maximum CPU time (in seconds) allowed will be enforeced if the "-cputime seconds" option is specified.
For example: sgplan -o p01-domain.pddl -f p01-s2-n1-l2-f50.pddl -out p01.soln -cputime 20
For more testing domains, try sgplan on the IPC-3 and IPC-4 benchmark suites.
The SGPlan 4
Planner (extended
abstract)
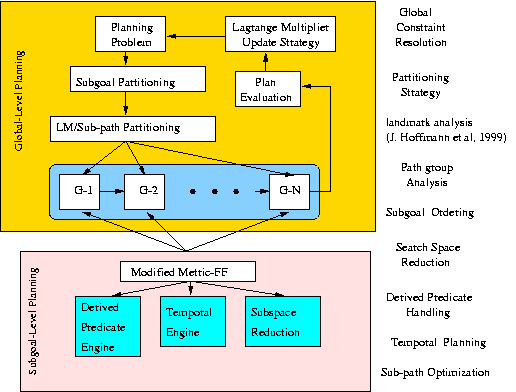
SGPlan 4 partitions a large planning problem into subproblems, each with its own subgoal, and resolves inconsistent solutions of subgoals using our extended saddle-point condition. Subgoal partitioning is effective because each partitioned subproblem involves a substantially smaller number of constraints (and exponentially smaller complexity) than that of the original problem. We have developed methods for the detection of reasonable orders among subgoals, a landmarks analysis to hierarchically decompose each subproblem, a search-space-reduction algorithm to eliminate irrelevant actions in subproblems, and a strategy to call the best planner to solve each bottom-level subproblem. Our current implementation of SGPlan 4 uses a modified Metric-FF planner for basic planning and only invokes LPG (2003 version) when the modified planner fails.
The Architecture of SGPlan 4
References:
- B. W. Wah and Y. Chen, Constraint Partitioning in Penalty Formulations for Solving Temporal Planning Problems, Artificial Intelligence, Elsevier, vol. 170, no. 3, pp. 187-231, 2006.
- Y. X. Chen, B. W. Wah, and C. W. Hsu, Temporal Planning using Subgoal Partitioning and Resolution in SGPlan, J. of Artificial Intelligence Research, vol. 26, Aug. 2006, pp. 323-369.
- B. W. Wah and Y. Chen, Subgoal Partitioning and Global Search for Solving Temporal Planning Problems in Mixed Space, Int'l J. of Artificial Intelligence Tools, World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd., vol. 13, no. 4, Dec. 2004, pp. 767-790.
- Y. Chen and B. W. Wah, Automated Planning and Scheduling using Calculus of Variations in Discrete Space, Proc. of Int’l Conf. on Automated Planning and Scheduling, 2003, pp. 2-11.
- B. W. Wah and Y. Chen, Partitioning of Temporal Planning Problems in Mixed Space using the Theory of Extended Saddle Points, Proc. 15th IEEE Int’l Conf. on Tools with Artificial Intelligence, 2003, pp. 266-273.
- C. W. Hsu, Y. X. Chen, and B. W. Wah, Subgoal Ordering and Granularity Control for Incremental Planning, Int'l J. of Artificial Intelligence Tools, World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd., 2006 (accepted to appear).
- Y. Chen, C. W. Hsu, and B. W. Wah, System Demonstration: Subgoal Partitioning and Resolution in SGPlan, System Demonstration Session, Int'l Conf. on Automated Planning and Scheduling, AAAI, June 2005, pp. 32-35.
- J. Koehler, J. Hoffmann, On Reasonable and Forced Goal Orderings and their Use in an Agenda-Driven Planning Algorithm, Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, Volume 12, 2000, pp. 338-386.
- J. Porteous, L. Sebastia, J. Hoffmann, On the Extraction, Ordering, and Usage of Landmarks in Planning, Proc. 6th European Conf. on Planning, 2001, pp. 37-48.
Acknowledgments:
Research supported by National Science Foundation Grant IIS 03-12084 and National Aeronautics and Space Administration Grant NCC 2-1230.